MWDM Filter
FAQs
An MWDM (Metro Wavelength Division Multiplexing) filter is an optical filter optimized for 5G fronthaul networks, designed to achieve high-density wavelength multiplexing through cost-effective solutions.
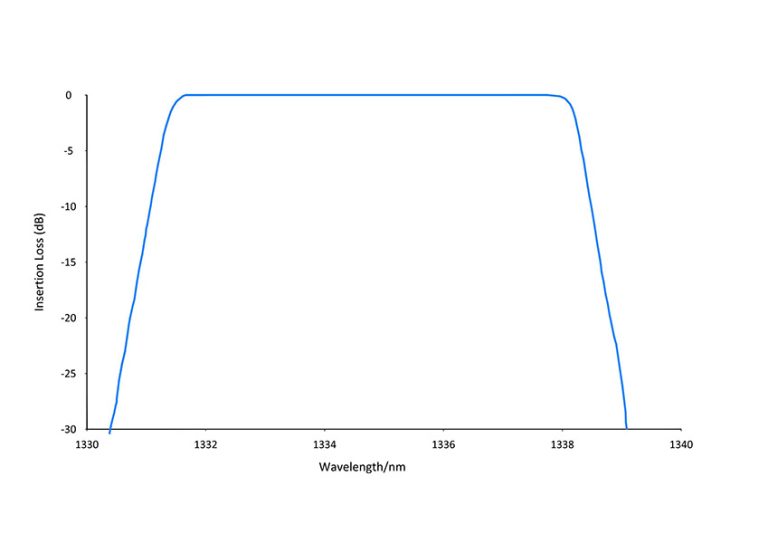
MWDM filters use six original CWDM wavelengths (e.g., 1271nm, 1291nm…1371nm, spaced 20nm apart), and apply thermal tuning (typically ±7°C) to shift each wavelength by ±10nm, generating two new channels per wavelength (e.g., 1271nm → 1261nm and 1281nm). This allows 12 channels (6 original × 2 tuned) to be multiplexed over a single fiber, increasing total capacity.
MWDM systems use 12 wavelength channels, covering the range from 1269.23nm to 1374.05nm, with approximately 10nm spacing between adjacent channels.
MWDM has 12 channels with 10nm spacing and relies on thermal tuning to generate additional channels. It is suitable for 5G fronthaul networks and metro networks.
CWDM has 18 channels with 20nm spacing and uses fixed wavelengths, ideal for enterprise networks and short-distance transmission.
When selecting an MWDM filter, key factors include center wavelength accuracy to match MWDM channels precisely and avoid crosstalk due to tuning errors. The filter must support ±7°C thermal tuning to stably generate half-wavelength spaced channels. Other considerations include insertion loss, isolation, and temperature stability.