Introduction: What Is Full-Band Infrared?
“Full-band infrared” typically refers to infrared technologies capable of detecting and imaging across the key spectral regions of the infrared spectrum, mainly including:
-
Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR)
-
Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR)
-
Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR)
-
Far Infrared (FIR)
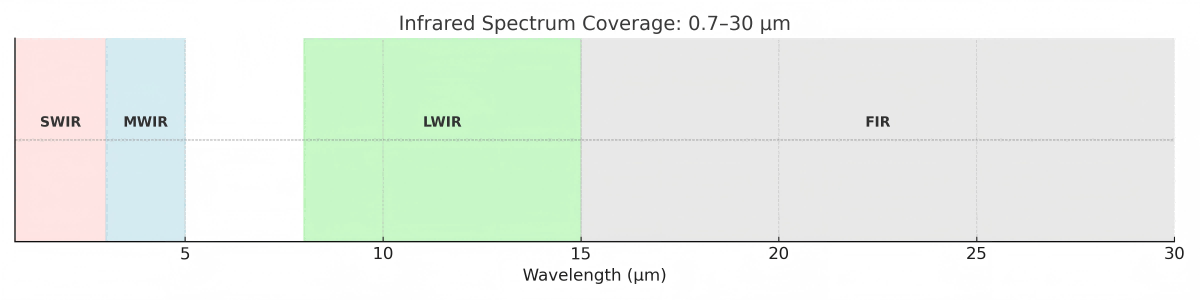
Infrared Spectrum Classification
- SWIR (Short-Wave Infrared): 1–3 μm SWIR partially overlaps with visible light and is sometimes referred to as near-infrared. It is sensitive to solar reflection and high-temperature targets.
- MWIR (Mid-Wave Infrared): 3–5 μm MWIR corresponds to peak thermal radiation from objects at room temperature. It is highly sensitive to temperature variations and ideal for thermal imaging.
- LWIR (Long-Wave Infrared): 8–15 μm This band is also a primary thermal emission range for ambient-temperature objects. Due to the atmospheric transmission window, LWIR enables clear thermal observation.
- FIR (Far Infrared): 15–1000 μm (focus: 15–30 μm) FIR lies beyond LWIR in the spectrum and corresponds to even lower-energy thermal emissions. It is suitable for detecting extremely cold objects and specific molecular vibration absorption bands.
Different infrared bands are influenced differently by atmospheric conditions. Targets may exhibit varying temperatures, emissivity, and reflectivity across the spectrum, making each band suitable for different applications.
Key Applications of Infrared Filters
SWIR Filters (0.7–3 μm)
-
Applications: Night vision, semiconductor inspection, agricultural imaging, material sorting, art authentication
-
Examples: SWIR cameras, silicon wafer inspection, crop health monitoring, plastic recycling
MWIR Filters (3–5 μm)
-
Applications: High-temperature thermal imaging, flame detection, gas monitoring, medical diagnostics
-
Examples: Military thermography, leaf temperature detection, CO/CO₂ gas sensing
LWIR Filters (8–15 μm)
-
Applications: Civil thermal imaging, autonomous driving, public safety, environmental monitoring
-
Examples: Thermal cameras, driver-assist systems, fever screening, ground temperature sensing
FIR Filters (15–30 μm)
-
Applications: Extreme low-temperature detection, gas spectroscopy, astronomy, superconductivity, fusion diagnostics

Our Infrared Filter Products (EUV to Far-IR)
-
Infrared dual-bandpass filters
Available Substrate Materials
| Material | Spectral Range | Key Features |
| Fused Silica | 0.2–2.5 μm | Low cost, high hardness |
| Silicon (Si) | 1.2–8.0 μm | High-temperature resistance, thermal stability |
| Zinc Selenide | 0.5–20 μm | Excellent full-range transmission |
| Sapphire | 0.15–5.5 μm | Wideband coverage, excellent mechanical strength |
Coating Technology: Ion-Assisted Deposition (IAD)
We utilize Ion-Assisted Deposition (IAD) to produce high-performance IR filters. This method introduces ion energy during evaporation to densify the coating and improve adhesion—ideal for multilayer precision filters used in:
-
Lidar
-
Optical communications
-
Aerospace remote sensing
-
FTIR spectroscopy
-
Industrial automation
How to Select the Right Infrared Filter
When selecting an infrared optical filter, consider the following:
-
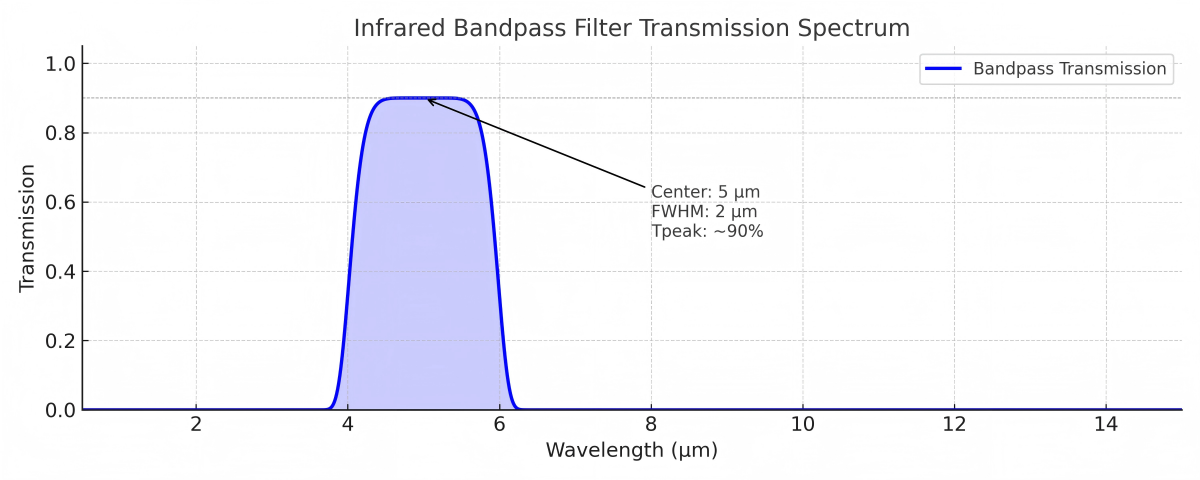
Center Wavelength & Bandwidth: Ensure the filter matches the target absorption peak or cutoff requirements.
-
Blocking Depth (Optical Density): Standard filters offer OD2 to OD3; higher blocking available upon request.
-
Angle of Incidence: Standard: 0° ± 5°. Custom filters available for tilted incidence.
-
Environmental Compatibility, Choose substrate based on environmental stress:
-
Humidity resistance: Si > Fused Silica > ZnSe > Ge
-
Thermal shock: Si > Fused Silica > ZnSe > CaF₂
-
Sand abrasion: Fused Silica > Si > Ge > ZnSe
-
The Industry Application We Served:
Our infrared filters are trusted by industries such as:
-
Aerospace
-
Medical imaging
-
Industrial automation
-
Consumer electronics
-
Smart home systems
-
Firefighting and rescue
Custom Orders Welcome
We offer custom-designed IR filters covering 0.7–30 μm. Contact us for consultation, samples, or technical specifications.







